Maths Class 10th Trigonometry Prove All Question With Easy Ways in Pdf
Chapter 8 of CBSE NCERT Class 10 Math covers Trigonometry. Concepts covered in Chapter 8 include trigonometric ratios, trigonometric ratios of complementary angles, trigonometric identities. The extra questions given below include questions akin to HOTS (Higher Order Thinking Skills) questions and exemplar questions of NCERT.
Here is a quick recap of the key concepts that are covered in this chapter in the CBSE NCERT Class 10 Math text book.
What are trigonometric ratios?
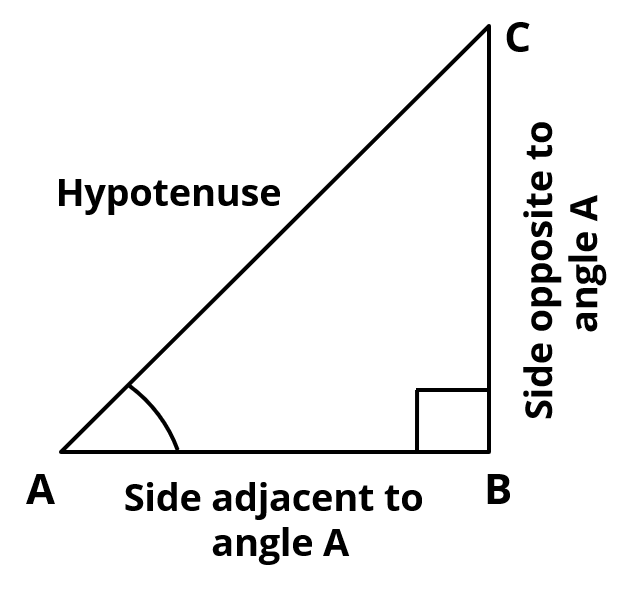
The trigonometric ratios of the angle A in right triangle ABC are defined as follows:
sine ∠A = \\frac{\text{side oppposite to angle A}}{\text{hypotenuse}}) = \\frac{\text{BC}}{\text{AC}})
cosine ∠A = \\frac{\text{side adjacent to angle A}}{\text{hypotenuse}}) = \\frac{\text{AB}}{\text{AC}})
tangent ∠A = \\frac{\text{side oppposite to angle A}}{\text{side adjacent to angle A}}) = \\frac{\text{BC}}{\text{AB}})
The ratios of cosec A, sec A and cot A are the reciprocals of sin A, cos A and tan A respectively.
cosecant ∠A = \\frac{\text{1}}{\text{sine of angle A}}) = \\frac{\text{AC}}{\text{BC}})
secant ∠A = \\frac{\text{1}}{\text{cosine of angle A}}) = \\frac{\text{AC}}{\text{AB}})
cotangent ∠A = \\frac{\text{1}}{\text{tangent of angle A}}) = \\frac{\text{AB}}{\text{BC}})
Trigonometric ratios of specific angles
The values of the trigonometric ratios of an angle do not vary with the lengths of the sides of the traiangle, if the angle remains the same.
| ∠A | 0° | 30° | 45° | 60° | 90° |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| sin A | 0 | \\frac{1}{2}) | \\frac{1}{{\sqrt{2}}}) | \\frac{{\sqrt{3}}}{2}) | 1 |
| cos A | 1 | \\frac{{\sqrt{3}}}{2}) | \\frac{1}{{\sqrt{2}}}) | \\frac{1}{2}) | 0 |
| tan A | 0 | \\frac{1}{{\sqrt{3}}}) | 1 | √3 | Not defined |
| cosec A | Not defined | 2 | √2 | \\frac{2}{{\sqrt{3}}}) | 1 |
| sec A | 1 | \\frac{2}{{\sqrt{3}}}) | √2 | 2 | Not defined |
| cot A | Not defined | √3 | 1 | \\frac{1}{{\sqrt{3}}}) | 0 |
∴ The value of sin A or cos A never exceeds 1, whereas the value of sec A or cosec A is always greater than or equal to 1
Trigonometric ratios of complementary angles:
The two angles are said to be complementary if their sum equals 90°.
The trigonometric ratios of complementary angles are as follows:
- sin(90° - A) = cos A
- tan(90° - A) = cot A
- sec(90° - A) = cosec A
- cos(90° - A) = sin A
- cot(90° - A) = tan A
- cosec(90° - A) = sec A
Trigonometric identities
An equation involving trigonometric ratios of an angle is said to be trigonometric idnetity, if it is true for all values of the angles involved.
Some of the key trigonometric identities used in this chapter are as follows:
- sin2 A + cos2 A = 1
- sec2 A =1 + tan2 A for 0° ≤ A ≤ 90°
- cosec2 A = 1 + cot2 A for 0° < A ≤ 90°
-
Question 1
Consider right triangle ABC, right angled at B. If AC = 17 units and BC = 8 units determine all the trigonometric ratios of angle C.
-
Question 2
Given sin A =\\frac{\text{12}}{\text{37}}), find cos A and tan A.
-
Question 3
If C and Z are acute angles and that cos C = cos Z prove that ∠C = ∠Z
-
Question 4
In ΔABC right angled at B, sin C = \\frac{\text{5}}{\text{13}}). Find :
(i) sin A
(ii) cos A
(iii) cos C
-
Question 5
In triangle ABC, right angled at B if sin A = \\frac{\text{1}}{\text{2}}), find the value of
1. sin C cos A - cos C sin A
2. cos A cos C + sin A sin C
-
Question 6
In triangle PQR, right angled at Q if PR = 41 units and PQ - QR = 31 find sec2R - tan2R.
-
Question 7
In triangle ABC right angled at B, AB = 12cm and ∠CAB = 60°. Determine the lengths of the other two sides.
-
Question 8
In a triangle ABC right angled at B, AB = 5 cm and AC = 10 cm. Determine ∠ BAC and ∠ BCA.
-
Question 9
sin (A + B) = 1 and sin (A - B) =\\frac{1}{2}) ; 0° < A + B ≤ 90°; ∠A > ∠B. Find ∠A and ∠B.
-
Question 10
Find the value of θ in each of the following. θ is an acute angle.
(i) 3 sec 2θ = 2√3
(ii) 4 cot 3θ - 4 = 0
(iii) 2 sin 2θ = 1
-
Question 11
Solve the following: 0 < θ < 90°
(i) 2 sin2 θ = \\frac{3}{2})
(ii) 3 tan2 θ + 2 = 3
(iii) cos2 θ - \\frac{1}{4})= \\frac{1}{2})
-
Question 12
Evaluate the following:
(i) cosec2 45° + tan2 45° - 3sin2 90°
(ii) cos 60° cos 30° - sin 60° sin 30°
(iii) \\frac{\text{tan 60° - tan 30°}}{\text{1 +tan 60° tan 30°}})
-
Question 13
Find the value of x in each of the following:
(i) cosec 3x = \\frac{\text{cot 30° + cot 60°}}{\text{1 + cot 30° cot 60°}})
(ii) cos x = 2 sin 45° cos 45° - sin 30°
-
Question 14
If θ is an acute angle and \\frac{\text{sinθ + 1 }}{\text{sinθ - 1}}) =\\frac{\text{√3 + 2 }}{\text{√3 - 2 }}), find θ.
-
Question 15
In an acute angle triangle ABC, sin (A + B - C) = \\frac{\text{1}}{\text{2}}), cot (A - B + C) = 0 and cos (B + C - A) =\\frac{\text{1}}{\text{2}}). What are the values of A, B, and C?
Source: https://practice-questions.maxtute.com/CBSE-Class-10-Math/trigonometry/
0 Response to "Maths Class 10th Trigonometry Prove All Question With Easy Ways in Pdf"
Post a Comment